Innovative techniques for fall prevention
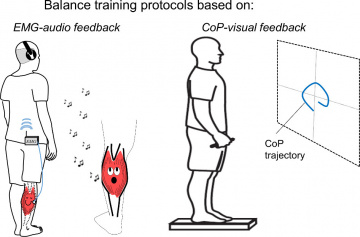
Falls are reported to occur at least once in a year for roughly 30% of people over 65. The spectrum of musculoskeletal consequences arising from falls ranges from light abrasions to hip fractures. Falls impact negatively on life quality, representing major burdens to the health care system. Gaining insights into how ageing may affect standing stabilization and improving balancing skills would likely help devising new strategies for fall prevention. To reach these goals our group has been working on the development of novel methodologies for the study and training of posture control, combining stabilometry with biofeedback techniques, based on surface electromyograms and center of pressure position (Figure).
Relevant publications:
Vieira T.M., Lemos T., Oliveira L.A.S., Horsczaruk C.H.R., Freitas G.R., Tovar-Moll F., Rodrigues E.C. Postural Muscle Unit Plasticity in Stroke Survivors: Altered Distribution of Gastrocnemius' Action Potentials, Front Neurol, vol. 10, pp. 686, 2019. hdl:11583/2744455
Dos Anjos F.V., Pinto T.P., Gazzoni M., Vieira T.M. The Spatial Distribution of Ankle Muscles Activity Discriminates Aged from Young Subjects during Standing, Front Hum Neurosci, vol. 11, pp. 190, 2017. hdl:11583/2670605
Vieira T.M., Baudry S., Botter A. Young, Healthy Subjects Can Reduce the Activity of Calf Muscles When Provided with EMG Biofeedback in Upright Stance, Front Physiol, vol. 7, pp. 158, 2016. hdl:11583/2643221
Agostini V. , Sbrollini A., Cavallini C., Busso A., Pignata G., Knaflitz M. The role of central vision in posture: Postural sway adaptations in Stargardt patients, Gait Posture, vol. 43, pp. 233-238, 2016. hdl:11583/2620705
Agostini V., Chiaramello E., Bredariol C., Cavallini C., Knaflitz M. Postural control after traumatic brain injury in patients with neuro-ophthalmic deficits, Gait Posture, vol. 34, pp. 248-253, 2011. hdl:11583/2426408
